How We Find and Correct Vertebral SubluxationsThe Atlas Orthogonal Chiropractic Approach
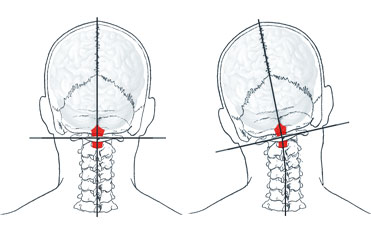
Over 30% of the sensory information needed to balance the body comes from the joints and muscles of the head and neck. The head is designed to be straight and the eyes to look level with the horizon. The center for equilibrium (balance) is located within the ears. Any misalignment in the neck drastically affects the body’s balance and equilibrium through neurological input and output. The brain will use the muscles to shift the entire spine in an effort to balance the head, eyes and ears to allow upright movement.
The ATLAS (C1) is the first cervical vertebrae of the spine.
ORTHOGONAL(or-thog’-ah-nal) means at right angles, or square. The head should sit level on the atlas and the atlas should sit squarely on the cervical spine (neck) The delicate upper neck, where the skull and atlas are located, is the most moveable and least stable area of the entire spine. An Atlas Orthogonal Chiropractor has received advanced training to identify and correct atlas misalignment with a precise, gentle adjustment with no popping or cracking of the neck.
Dr. Lavender and Dr. Jarman each have over 20 years experience as BoardCertifiedAtlasOrthogonal Chiropractors (B.C.A.O.) To learn more about the Atlas Orthogonal Technique go to: www.globalao.com
TRT Torque Release Technique
 "TRT" has been designed as part of scientific research into the health benefits of chiropractic. As such it is a mixture of the best of existing chiropractic techniques and principles, quantum physics and the body/mind connection. Creating the first integrated chiropractic system for the second century of chiropractic.
"TRT" has been designed as part of scientific research into the health benefits of chiropractic. As such it is a mixture of the best of existing chiropractic techniques and principles, quantum physics and the body/mind connection. Creating the first integrated chiropractic system for the second century of chiropractic.
To learn more about Torque Release Technique go to:www.torquerelease.com This is a system of spinal evaluation combined with a handheld adjusting instrument that delivers a consistent, low-force thrust.Thompson Terminal Point technique is a system of analysis and a special table that reduces the amount of energy needed to adjust your spine.
A.M.I.T.Advanced Muscle Integration Technique
Click Here to Learn more about A.M.I.T.
The AMIT system of analysis performs a functional evaluation of 720 muscles in the body. Treatment follows to restore the injured or affected area. In simple terms, when a muscle is overstressed beyond its ability to handle a load, the tissue either tears or is neurologically inhibited. This condition is defined as either “Arthrogenic Muscle Inhibition” (AMI) or “Neuro-Proprioceptive Inhibition” (NPI). AMI is caused when the joint is injured or inflamed. NPI is caused when a muscle or connective tissue is injured.
How can AMIT help me?
AMIT treats the inhibition that takes place in nerve centers called proprioceptors. These centers called “intelligent terminals” monitor tension, stretch, motion, and pressure. When the system is traumatized or inflamed, these centers “trip”, much like a circuit breaker in an electrical circuit. Once this occurs, the muscle stays inhibited when it is placed under load. Loss of range of motion, pain, and weakness are experienced. When this happens, other muscles or tissues attempt to take on more of the load as the body adapts and compensates.
After the NPI muscle is defined by the doctor, stimulation of eight separate reflex centers and adjustment of three spinal segments, re-activates proper neurological function for that muscle. In the case of AMI, manipulation of the joint can re-establish the normal feedback receptors and the muscle associated with that joint to reactivate in pain-free motion. Once reactivated, the muscles are now prepared to respond to strengthening exercises. Using AMIT, the body is aided in the support it needs to heal and perform optimally.
When a muscle is overloaded beyond its ability to sustain the load, one of two things happen. The muscle fibers tear and/or the nervous system inhibits the muscle. Much like a circuit breaker in an electrical circuit. This is done to protect the muscle from more severe injury. If the inhibited muscle is loaded again during physical activity it will not be able to contract appropriately to support the force applied and will be weak. If the muscle continues to be stressed, the body will create pain so as to avoid more damage. This can also occur when a joint is swollen, inflamed or injured setting up what is identified as “Arthrogenic Muscle Inhibition” (AMI). The process of AMI occurs when a joint is swollen, inflamed or injured, any muscle that attaches to the joint or crosses over the joint will become inhibited. This is common in post-surgical cases and explains why rehabilitation is slow or reaches an unacceptable plateau. Once a muscle is inhibited, the central nervous system develops an adaptive strategy to use other muscles or tissues to take on more of the load. This leads to adaptive movement patterns and is called “recruitment” or “adaptation”.
The adapted tissue becomes the next site of injury and the injury/adaptation cycle continues. Eventually, there will be no muscles in an area to adapt to. This places more stress on the ligaments and connective tissues and they begin to break down more rapidly. This leads to degenerative changes in the joint.
Objective precision neurological muscle testing is the backbone of the AMIT system. Testing of isolated muscles assesses the function of individual muscles to determine if they are inhibited or functional. This defines positions of instability.
Muscle overload occurs because of:
- -Lack of conditioning to the level of demand.
- -Traumatic force exceeds the integrity of the muscle or tissues.
- -Neurological inhibition
- -Proprioceptive inhibition
- -Nutritional deficiencies and excesses.
- -Acupuncture system imbalances
- -Overuse
- -Dehydration
- -Organ/gland stress
- -Emotional stress
- -Sleep deprivation
- -Disease
- -Medications
- -Ice
- -Physical therapy modalities
- -Toxic overload
- -Training and conditioning imbalances





